How Does the Energy Rating Software Calculate a 7-Star Energy Rating?
There are four accredited softwares that can be used to prepare a 7 star energy rating report. Accurate, HERO, FirstRate 5 and Bers Pro. The option to prepare an energy rating to assess the dwellings thermal performance provides a more accurate energy assessment over the elemental provision pathway found in the NCC 2022: Part H because it assesses the design as a whole and how the layout, the orientation, climate data and the surrounding ostructions all come into play.
The climate region has a set thermostat range that is considered the ideal temperature for both the warm months and the cold months. The software determines how much artificial heating is required in the colder months to keep within the temperature range. The software also determines how much artificial cooling is required in the warmer months to keep within the temperature range. Essentially, the more artificial heating or cooling, the lower the star rating result. A higher star rating predicts less intervention of heating or air conditioning.
To understand the software and how it works, read this guide.
Energy Rating Software: A Brief Introduction
Software is essential to any energy rating assessment, making the whole process much more efficient and accurate over the elemental provisions pathway (NCC Vol.2 Part:H). Australia has 69 NatHERS climate zones that assesses the building fabric using the Cheneth engine, so the software must be smart enough to assess all the variables.
The Nationwide House Energy Rating Scheme (NatHERS) uses software that complies with 68 years of scientific research by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO). The CSIRO is an Australian body that researches various areas, including energy, and how it can be used for commercial and industrial applications.
NatHERS has around 600 assessors nationwide that only use one of the four tools approved by the institution. These software programs use CSIRO’s physics engine, the most prominent example being AccuRate, software designed by CSIRO.
How Does the Energy Rating Software Work?
The energy rating software works its magic when assessors input relevant data, which is a must-have to build a more sustainable home. The data points relate to various thermal factors, such as building orientation, local climate, and construction and design, including floors, walls, windows, ceilings, etc.
Let’s discuss the details of zonal data generated from NatHERS’s software, which helps assessors determine a dwelling’s thermal performance.
Internal Heat Generation
According to NatHERS, heat loads inside a home result from latent heat generated by occupants, air moisture, cooking, lighting, and electrical appliances. The software can determine how well each zone in the house will perform by assigning occupancy and conditioning rules (staying within a comfortable temperature range).
Here are some of the different zones inside a home that this software studies.
1. Kitchen
NatHERS only allows one kitchen zone. The heat generated by the kitchen zone can benefit the residents when the temperature drops in the evening. There might not be a need to turn on the heater, especially when the kitchen is connected to the living zone.
Tip: Making the kitchen bigger will improve the star rating.
2. Living Zone
Living zones are considered daytime zones in the NatHERS software, and you can select only two of them, no matter how many you have. Since they do not have any occupancy heat, you’ll be turning on the heater, which affects the energy rating.
Tip: Keep them modestly sized and as close to the kitchen as possible to reduce heating requirements.
3. Bedroom Zone
Bedrooms are small, so they have a low energy load. They are usually conditioned during the night, which results in energy savings.
Tip: Houses with more bedrooms typically have a higher star rating, although it is not guaranteed.
4. Daytime Zone
Any space outside the above categories is considered part of the daytime zone. This usually includes bathrooms with openable windows, studies, hallways, and entries. Daytime zones are often the most inefficient spaces, so keeping them to a minimum improves their thermal performance.
Tip: Design bathrooms and laundries with open windows to make them part of the unconditioned zone.
5. Unconditioned Zone
As described above, an unconditioned zone has no heating or cooling requirements, such as a garage or a bathroom with openable windows.
Tip: Make as many daytime zones unconditioned as possible to improve the thermal performance of a dwelling.
6. Night-time Zone
Nighttime zones, such as an en-suite, can be accessed from the bedroom. Due to their small size, they require less energy.
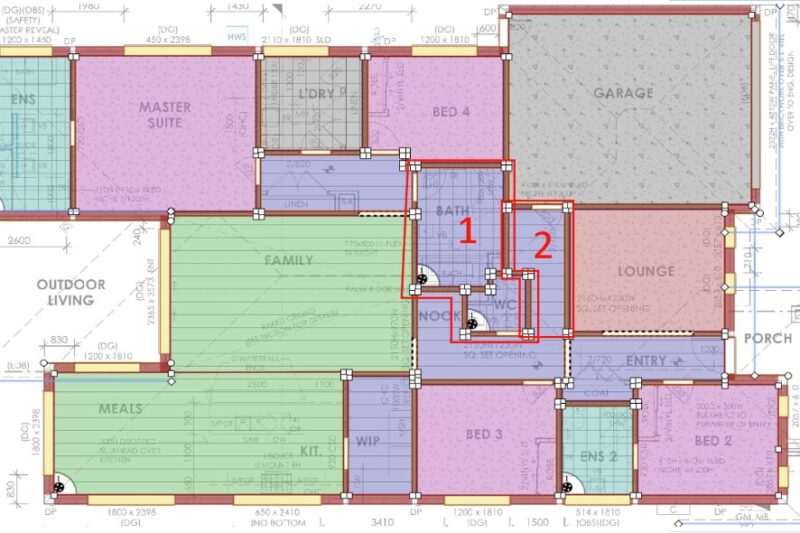
A Visual Example
If you look at the building drawing below, the builder has internally located the water closet and the bathroom. This design is highly inefficient because it makes them both daytime zones. Instead, moving them to the external building footprint near the laundry is much better for making them an unconditioned zone.
The entry and the associated hallway leading to the garage door are also unnecessary daytime zones. The builder should eliminate this hallway, increasing the size of the living space and improving the occupancy gains.

Determining Heating and Cooling Loads Using Software
Using the energy rating software, the assessor determines each room’s heating and cooling load. Focusing on these zones helps them understand if a particular room falls within the allowed range and whether it should be tweaked to achieve a higher star rating.
The Sliding Scale System
The sliding scale system tells you how much insulation and glazing upgrades will help a homeowner achieve a 7-star rating based on their existing base specifications. It is crucial to note that there is a limit to how many upgrades one can make. If the house’s base specifications are below a certain threshold, it cannot achieve the 7-star rating, no matter how much money one spends on the upgrades.
The graph below, containing blue and orange lines, shows how much insulation and glazing upgrades are needed to achieve the 7-star rating. The ideal home with high base specifications requiring zero upgrades is on the leftmost. As you move to the right, the orange line keeps increasing, which means the house needs more tweaks and upgrades.
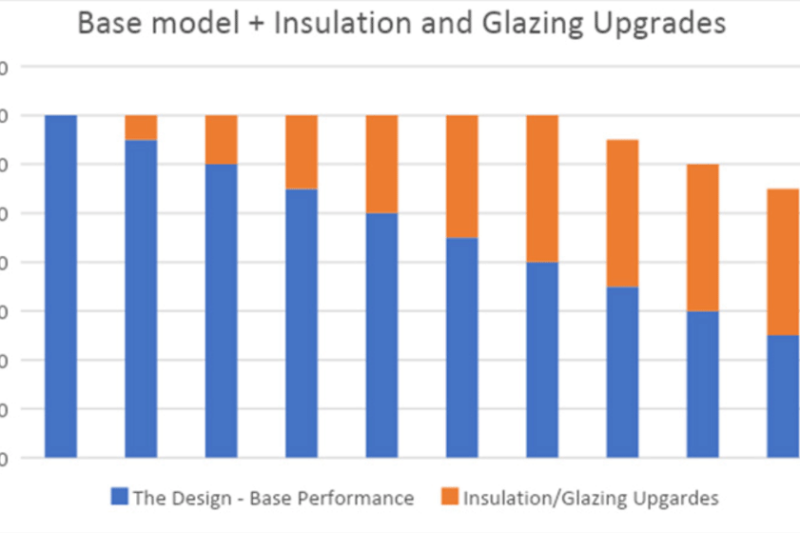
As the graph suggests, reaching a 7-star rating is impossible if a house’s base specifications are below 4 stars.
Conclusion
The software for determining a dwelling’s energy rating has come a long way, where entering a few numbers gives quality results without any manual headache. If you are a builder or an architect wanting to assess your constructions accurately, it is crucial to pair quality software with a responsible assessor.
That is where PassivEnergy comes in. We are a name in sustainable construction and building that you can fully trust. With state-of-the-art 7-star assessments, we help you design compliant and comfortable houses for occupants. Firstrate5 software is the industry-leading tool we use, which is NatHERS-approved and provides highly accurate assessments.
So, get your construction plans assessed by PassivEnergy and create a sustainable future.